
- #WINDOWS 7 REARM COMMAND HOW TO#
- #WINDOWS 7 REARM COMMAND TRIAL#
- #WINDOWS 7 REARM COMMAND WINDOWS 7#
Now the Image is ready to deploy and the KMS server will receive different CMID’s from the servers. You can reset your rearm count up to 4 times, each slmgr /rearm command give you another 30 days everytime your rearm count is over use the following. Now set make sure the Skiprearm is set to 0 at the following location: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\WindowsNT\CurrentVersion\SoftwareProtectionPlatform
#WINDOWS 7 REARM COMMAND TRIAL#
The C-drive is used as a recovery partition. Method 1: Command Prompt Method to Reset and Extend Windows 7, Windows 8/8.1 Trial Period upto One Year Open command prompt with administrative privilege. The process is not very complicated but requires little patience.
#WINDOWS 7 REARM COMMAND WINDOWS 7#
Well, you can reset your Rearm count and run Windows 7 forever without cracking it actually. In this period, you need to activate it (which is generally cracked).
#WINDOWS 7 REARM COMMAND HOW TO#
Knowing this we searched how to reset the Rearm count and found an article that explained how we could reset the rearm count. Now provide following command: slmgr -rearm. which means that when you set SkipRearm then you don’t rearm the machine. We discovered that the “Remaining Windows Rearm Count” was 0. When testing this we discovered that the CMID keeps the same after rearming the Windows machine.
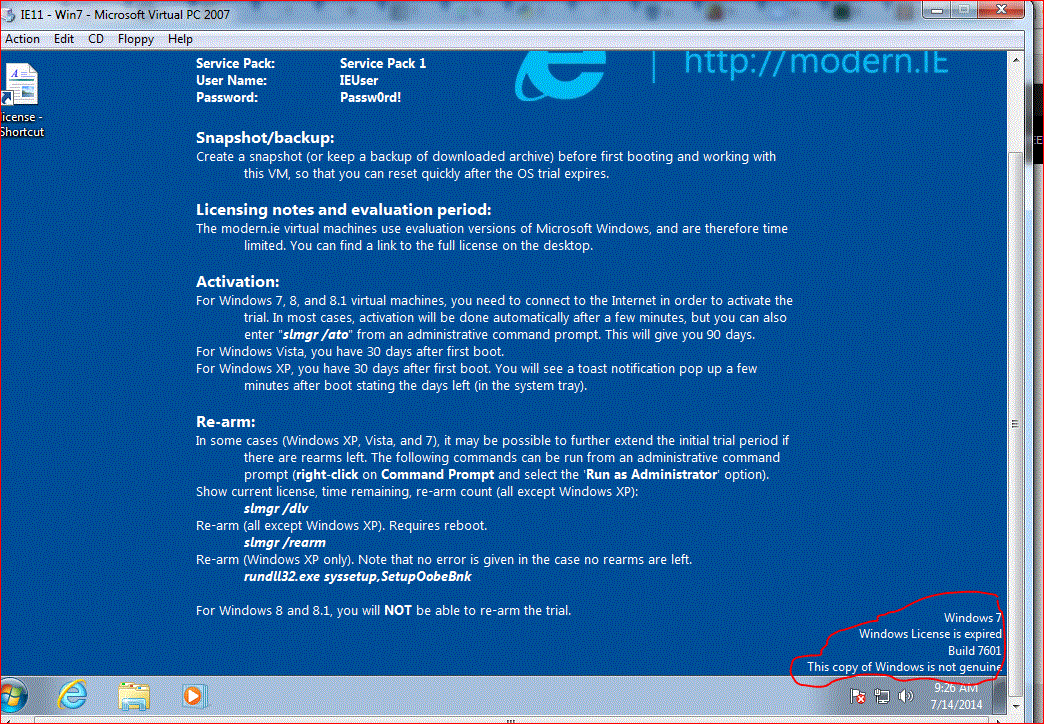
We searched for a solution and everyone mentioned rearming the machine, but then we received the message that we can’t rearm. We then searched for a solution but everyone was pointing out to set the Skiprearm to 1. A different CMID is needed to activate using KMS services. Now to check the current license, time remaining, rearm count use the command. We need to reboot the system for the changes to take effect. When working with Machine Creation Services we discovered that the Clients all have the same CMID. Never fear, I can extend the trial period by running the following command from an administrative command prompt.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
